
Ancient Egypt
The Ancient Egyptians flourished along the Nile River in northeastern Africa over 4,000 years ago. They established a powerful civilization known for its impressive pyramids, complex religious beliefs, and advancements in art, medicine, and engineering. Ancient Egypt developed hieroglyphic writing, papyrus paper, and irrigation techniques. Their belief in the afterlife resulted in the construction of elaborate tombs, such as the Great Pyramid of Giza.
The name Amun meant "the hidden one”. He represented all the mysterious things in the universe and he was invisible like the air or the wind.
Sekhmet was one of the oldest known Egyptian deities. Sekhmet's name means "she who is powerful," and she was both a warrior goddess and the patron of healers.
Maat was the daughter of Ra and the wife of Thoth. She weighed the heart of those who died against her feather to decide who would travel to the afterlife. She is depicted as a woman with an ostrich feather on her head, sometimes winged. Sometimes she was pictured as an ostrich feather.
Ancient Egyptians believed symbols did more than relay information, they were an important part of the Ancient Egyptian religion. Icons that represented different gods and goddesses of Ancient Egypt also represented different religious values. For example, the feather of the goddess Ma'at represented truth and justice.
This free set of interactive task cards is an engaging way to teach middle school students about Ancient Egypt.
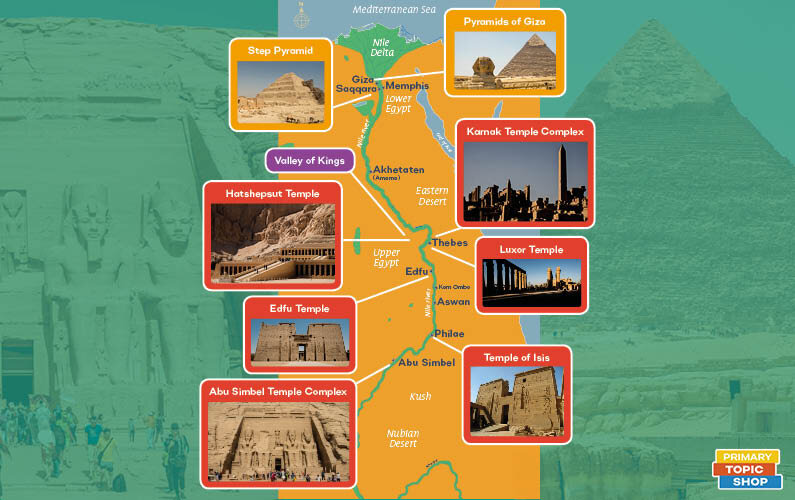
When we lived in Egypt, we were lucky enough to visit several ancient sites, some of which were more than 4,500 years old. We have used the photos and knowledge we gained during these travels to make our Ancient Egypt teaching resources.






Papyrus is not only the name of the plant, but also the paper that is made from the plant. Papyrus was used to make paper as early as 3,000 BC and was used for thousands of years.
Follow these step-by-step instructions to make your own papyrus!